Mites, are small arthropod belonging to the subclass acari (also known as Acarina) and the class arachnida. In soil ecosystems, mites are favored by high organic matter content and by moist conditions, where in they actively engage in the fragmentation and mixing of organic matter.
LIFE CYCLE OF MITES
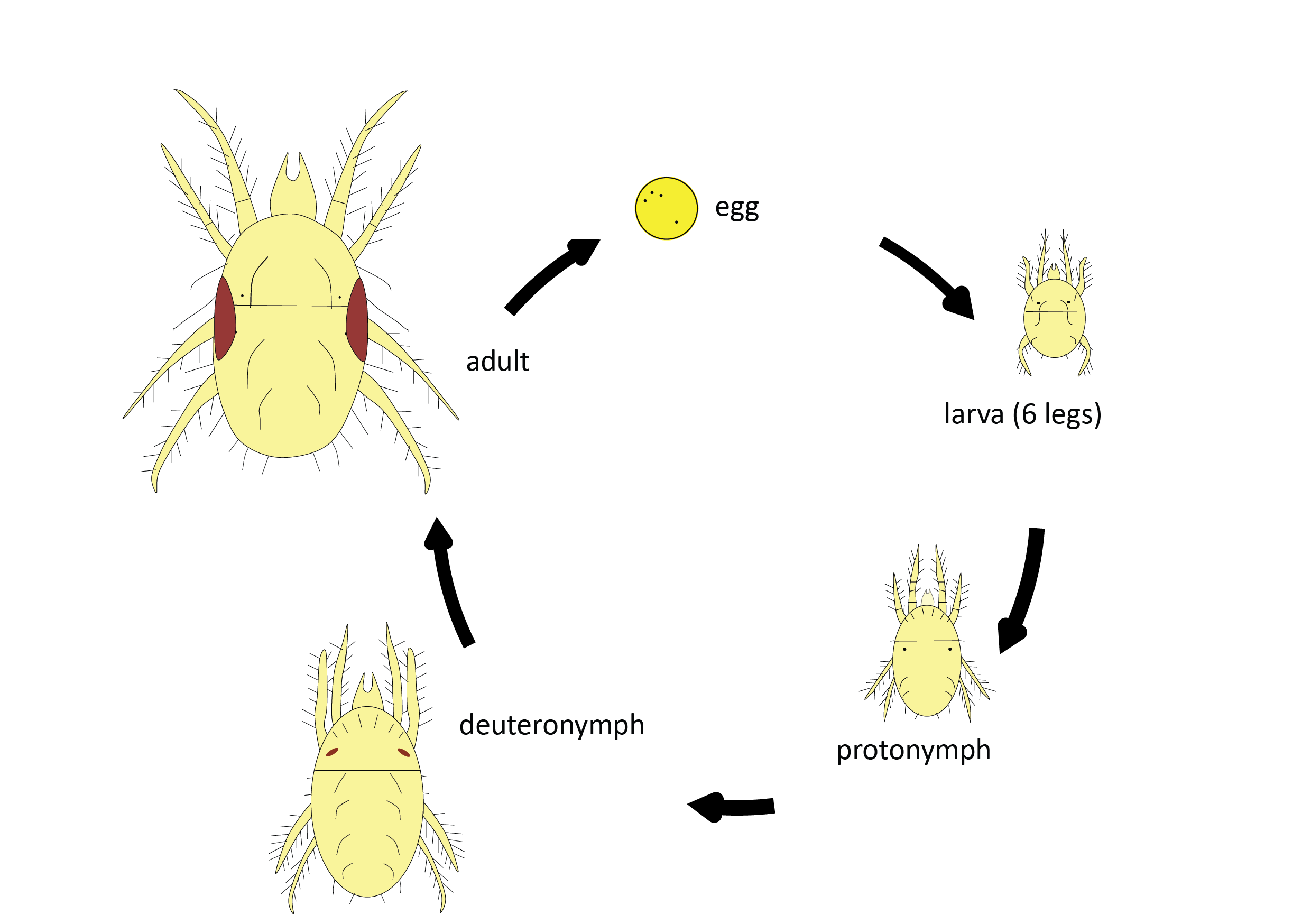
•Scabies, a mite infestation causing itching and irritation, often lead to secondary infections induced by scratching.
•Scabies is cause by female (Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis) burrowing, after mating, into epidermal stratum corneum, where she feeds on lymph. There she lays the eggs and leaves scybala (fecal material).
DISEASES CAUSE BY MITES
HOW TO CONTROL
•Depend on type of mite.
•Host-related can be reduced by controlling the HOST itself (birds, rats, house mice) by modifying buildings. Trapping and poisoning.
•Keeping grasses cut short and removing vegetable near buildings.
•Pesticides for outdoor residual treatment.
•Repellent
•Personal hygiene
•Hot water and soap who infected.
No comments:
Post a Comment